
What is Diabetic Dyslipidemia?
This page may contain affiliate links. If you choose to purchase after clicking a link, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
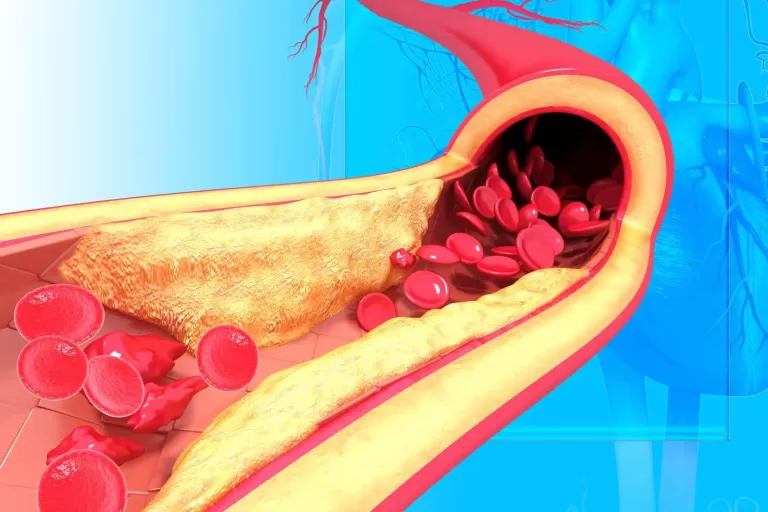
Diabetic dyslipidemia is a condition that occurs when a person with diabetes has abnormal levels of lipids (fats) in their blood. This condition is characterised by lower levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, as well as triglycerides.
HDL cholesterol is what some experts call “good” cholesterol, while LDL cholesterol is what they refer to as “bad” cholesterol. When a person’s LDL cholesterol levels rise too high, LDL cholesterol can form plaques that narrow or block blood vessels. As a result, individuals are at a higher risk of cardiovascular disease or stroke.
Read: Cholesterol levels explained
Diabetic dyslipidemia is caused by insulin resistance, which is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance can lead to an increase in the production of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles in the liver. These particles are then converted into LDL particles, which can cause plaque buildup in the arteries.
It is important to get regular lipid profile tests to monitor your lipid levels. The National Library of Medicine (NLM) suggests the following healthy cholesterol levels for adults: Total cholesterol: 125-200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl), Non-HDL cholesterol: less than 130 mg/dl, LDL cholesterol: less than 100 mg/dl, Total HDL cholesterol: The healthy level varies by sex: for biological males, it is 40 mg/dl or higher, and for biological females, it is 50 mg/dl or higher.
To help maintain healthy lipid levels, it is important to follow a healthy diet and exercise regularly. Foods that are good for lowering LDL cholesterol include whole grains, fruits and vegetables, nuts and seeds, and fish high in omega-3 fatty acids. Foods to avoid include saturated fats and trans fats .




Leave a Comment