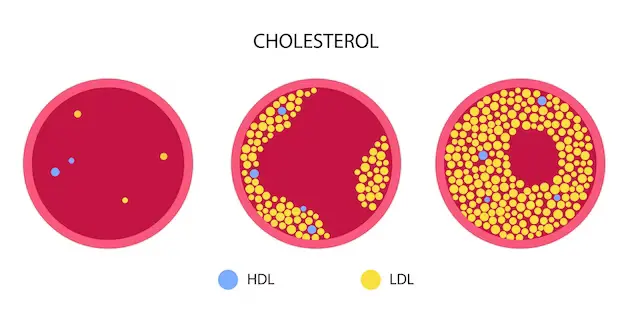
Cholesterol is a fatty substance that is produced by the liver and is essential for the proper functioning of the body. However, having high levels of cholesterol can lead to heart disease and other health problems. The recommended total cholesterol levels are under 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for most adults and under 170 mg/dL for children.
Cholesterol is carried in the blood by lipoproteins. There are two main types of lipoproteins: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because it can build up in the walls of arteries, leading to atherosclerosis and heart disease. HDL on the other hand, is often referred to as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove LDL from the bloodstream.
Here are some steps that adults can take to maintain healthy cholesterol levels:
Eat a healthy diet
A diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for maintaining good health. Here are some examples of each food group and why they are good for the body:
Healthy Fruits:
- Apples: Apples are rich in fiber and antioxidants that help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Blueberries: Blueberries are high in antioxidants and have been shown to improve brain function and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Bananas: Bananas are a great source of potassium, which helps regulate blood pressure and support heart health.
Healthy Vegetables:
- Spinach: Spinach is packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help protect against chronic diseases.
- Carrots: Carrots are rich in beta carotene, which is converted into vitamin A in the body. Vitamin A is essential for healthy vision and immune function.
- Broccoli: Broccoli is high in fiber, vitamins C and K, and sulforaphane, a compound that has been shown to have anti-cancer properties.
Healthy Whole Grains:
- Oats: Oats are high in fiber and beta-glucans, which help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health⁷.
- Whole Wheat: Whole wheat is rich in antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. It has been linked to lower risks of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer, and more.
- Brown Rice: Brown rice is a good source of fiber and has been shown to help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Healthy Lean Proteins:
- White-fleshed fish: White-fleshed fish such as cod and halibut are excellent sources of hunger-satisfying protein with little fat and relatively few calories. Other types of fish such as salmon have higher amounts of healthy omega-3 fats.
- Plain Greek yogurt: Greek yogurt is packed with protein and contains less sugar than regular yogurt. It’s also a great source of probiotics that help support gut health.
- Beans, peas, and lentils: These plant-based proteins are high in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They have been shown to help reduce the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer, and more.
Healthy Fats:
- Avocado: Avocado is high in monounsaturated fats that help reduce inflammation in the body. It’s also a good source of fiber and potassium.
- Nuts: Nuts such as almonds, walnuts, and pistachios are high in healthy fats that help reduce inflammation in the body. They’re also a good source of protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Olive Oil: Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats that help reduce inflammation in the body. It’s also a good source of vitamin E and antioxidants that help protect against chronic diseases.
Exercise regularly
Regular physical activity can help raise HDL cholesterol levels and lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Here are some examples of exercises and physical activities that can help:
Walking: Walking is a low-impact exercise that can be done almost anywhere and is suitable for people of all ages and fitness levels. It has been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Jogging/Running: Jogging or running is a high-impact exercise that can help improve cardiovascular health and lower LDL cholesterol levels. It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your runs to avoid injury.
Biking: Biking is a low-impact exercise that can be done indoors or outdoors. It’s a great way to improve cardiovascular health and lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Swimming: Swimming is a low-impact exercise that is easy on the joints and can help improve cardiovascular health and lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Lifting weights: Strength training exercises such as lifting weights or using resistance bands can help build muscle mass, increase metabolism, and lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Yoga: Yoga is a low-impact exercise that can help reduce stress, improve flexibility, and lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Maintain a healthy weight
Being overweight or obese can increase LDL cholesterol levels.
Quit smoking
Cigarette smoke contains thousands of chemicals that can damage blood vessels and increase cholesterol levels, making it harder for the body to remove unhealthy cholesterol from the blood. Smoking can raise LDL (low-density lipoprotein) or “bad” cholesterol levels and lower HDL (high-density lipoprotein) or “good” cholesterol levels.
Over time, this can lead to inflammation in blood vessels and arteries, and plaque can build up in arteries, which can harden and break off, leading to blood clots and strokes. Quitting smoking can improve cholesterol levels and decrease the risk of cardiovascular events.
Limit alcohol intake
Drinking too much alcohol can increase triglyceride levels, which can raise the risk of heart disease.
Triglycerides are a type of fat that is found in the blood and are used by the body for energy. However, when triglyceride levels are too high, they can build up in the walls of arteries, leading to atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Alcohol is metabolized by the liver, which converts it into triglycerides and cholesterol. When alcohol is consumed in excess, it can cause an increase in triglyceride levels in the blood. This is because the liver is unable to process all of the triglycerides that are produced from alcohol metabolism. Over time, this can lead to an accumulation of triglycerides in the blood, which can increase the risk of heart disease.
It’s important to note that moderate alcohol consumption has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. However, heavy drinking can have negative effects on cholesterol levels and overall health. If you drink alcohol, it’s important to do so in moderation and talk to your doctor about what amount is safe for you.
Summing up
It’s important to note that some people may need medication to help lower their cholesterol levels. If you have high cholesterol or other risk factors for heart disease, talk to your doctor about what steps you can take to maintain healthy cholesterol levels.






Cholesterol levels explained